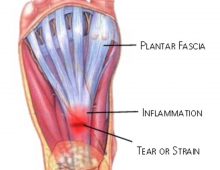
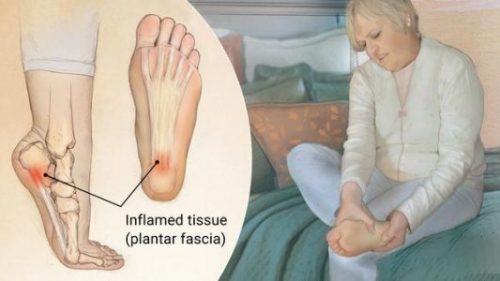
Plantar Fasciitis Overview:
Plantar Fasciitis is an inflammation of a thick band of tissue that connects the heel bone to the toes.
- Very common. More than 3 million US cases per year
- Usually self-treatable
- Usually self-diagnosable
Lab tests or imaging rarely required. Usually self-diagnosable. Symptoms include stabbing pain near the heel. Pain might be worst in the morning.
What is the main cause of plantar fasciitis?
Plantar fasciitis (inflammation to the plantar fascia ligament) is most commonly caused by strain injury causing micro tears to the ligament as it attaches to the heel bone or other areas of tightness on the sole of the foot.
Treatment consists of therapy and self care
Treatments include physical therapy, shoe inserts, steroid injections, and surgery.
Therapies
Stretching, Physical therapy, and Massage
Stretching
Stretching exercises can improve flexibility and improve physical function.
Physical therapy
Restores muscle strength and function through exercise.
Massage
Relaxes tense muscles.
Medications
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug and Steroid
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug
Relieves pain, decreases inflammation, and reduces fever.
Common drugs
Ibuprofen
It can treat fever and mild to severe pain.
Naproxen
It can treat fever and pain.
Steroid
Modifies or simulates hormone effects, often to reduce inflammation or for tissue growth and repair.
Common drugs
Methylprednisolone
It can treat inflammation, severe allergies, flares of chronic illnesses, and many other medical problems. It can also decrease some symptoms of cancer.
Self-care
RICE (Rest, Ice, Compression, Elevation), Shoe modification, Physical exercise, and Activity modifications
RICE (Rest, Ice, Compression, Elevation)
Rest, ice, compression, and elevation. A first-aid treatment for sprains and strains.
Shoe modification
Selecting shoes that fit properly and provide arch support.
Physical exercise
Aerobic activity for 20-30 minutes 5 days a week improves cardiovascular health. If injured, pursuing an activity that avoids the injured muscle group or joint can help maintain physical function while recovering.
Activity modifications
Adjusting amount or type of physical activity to avoid aggravating a condition.
Devices
Brace and Splint
Brace
A device applied to the body to help stabilize, protect, or limit movement of a damaged joint.
Splint
A rigid accessory used to stabilize and protect an injured joint.
Specialists
Podiatrist, Sports medicine, Physical therapist, and Primary care provider (PCP)